2
Christopher Brooks
2.1 Introduction
As noted in the last chapter, the Mesopotamians regarded the gods as cruel and arbitrary and thought that human existence was not a very pleasant experience. This attitude was not only shaped by all of the things that ancient people did not understand, like disease, weather, and death itself, but by the simple fact that it was often difficult to live next to the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, which flooded unpredictably and necessitated constant work in order to be useful for irrigation. Likewise, the threat of invasion from both rival cities and from foreigners (both “barbarians” and more organized groups) threatened to disrupt whatever stability existed. Life for most Mesopotamians, especially the vast majority who were common farmers, was not easy.
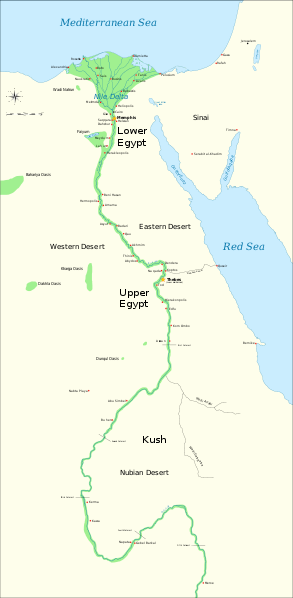
Things were a bit different in the other great ancient civilization of the eastern Mediterranean: Egypt, whose civilization developed along the banks of the Nile river. The Nile is the world’s longest river, stretching over 4,000 miles from its mouth in the Mediterranean to its origin in Lake Victoria in Central Africa. Because of consistent weather patterns, the Nile floods every year at just about the same time (late summer), depositing enormous amounts of mud and silt along its banks and making it one of the most fertile regions in the world. The essential source of energy for the Egyptians was thus something that could be predicted and planned for in a way that was impossible in Mesopotamia. There is a direct connection between this predictability and the incredible stability of Egyptian civilization, which (despite new kings and new dynasties and the occasional foreign invasion) remained remarkably stable and consistent for thousands of years.
Key Terms for Identification 2.1 – 2.2
- Kemet
- pharaoh
- Nile River
- ma’at
- Hatshepsut
- Amenhotep IV a.k.a. Akenaten
- Tutankhamun
- Ramses II
- Hyksos
- viziers
- “sea peoples”
The Egyptians themselves called the Nile valley “Kemet,” the Black Land, because of the annually-renewed black soil that arrived with the flood. For the most part, this was ancient Egypt: a swath of land between 10 and 20 miles wide (and in some places merely 1 or 2 miles wide) made up of incredibly fertile soil that relied on the floods of the Nile. This land was so agriculturally productive that Egyptian peasants could bring in harvests three times as bountiful of those in other regions like Mesopotamia. In turn, this created an enormous surplus of wealth for the royal government, which had the right to tax and redistribute it (as did the Mesopotamian states to the east). Beyond that strip of land were deserts populated by people the Egyptians simply dismissed as “bandits” – meaning nomads and tribal groups, not just robbers.
There were three major periods in ancient Egyptian history, the time during which Egypt was not subject to foreign powers and during which it developed its distinctive culture and built its spectacular examples of monumental architecture: the Old Kingdom (2680 – 2200 BCE), the Middle Kingdom (2040 – 1720 BCE), and the New Kingdom (1550 – 1150 BCE). There were also two “intermediate periods” between the Old and Middle Kingdoms (The First Intermediate Period, 2200 – 2040 BCE) and Middle and New Kingdoms (The Second Intermediate Period, 1720 – 1550 BCE). These were periods during which the political control of the ruling dynasty broke down and rival groups fought for control. The very large overarching story of ancient Egyptian history is that each of the different major kingdoms was quite stable and relatively peaceful, while the intermediary periods were troubled, violent, and chaotic. The remarkable thing about the history overall is the simple fact of its longevity; even compared to other ancient cultures (Mesopotamia, for instance), Egyptian politics were incredibly consistent.
The concept of these different periods was created by Manetho, an Egyptian priest who, in about 300 BCE, recorded the “definitive” history of the ancient kings and created the very notion of the old, middle, and new kingdoms. While that periodization overlooks some of the specifics of Egyptian history, it is still the preferred method for dating ancient Egypt to this day because of its simplicity and clarity.
Also, a note on nomenclature: the term “pharaoh” means “great house,” the term used for the royal palace and its vast supporting bureaucracy. It came to be used to refer to the king himself starting in the New Kingdom period; it would be as if the American president was called “the White House” in everyday language. This chapter will use the term “king” for the kings of Egypt leading up to the New Kingdom, then “pharaoh” for the New Kingdom rulers to reflect the accurate use of the term.
2.2 The Political history of ancient Egypt
Egypt was divided between “Upper Egypt,” the southern stretch of the Nile Valley that relied on the Nile floods for irrigation, and “Lower Egypt,” the enormous delta region where the Nile meets the Mediterranean. The two regions had been politically distinct for centuries, but (according to both archeology and the dating system created by Manetho) in roughly 3100 BCE Narmer, a king of Upper Egypt, conquered Lower Egypt and united the country for the first time. The date used for the founding of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, 2680 BCE, is when the third royal dynasty to rule all of Egypt established itself. Its king, Djoser, was the first to commission an enormous tomb to house his remains when he died: the first pyramid. The Old Kingdom represented a long, unbroken line of kings that presided over the first full flowering of Egyptian culture, architecture, and prosperity.
The Old Kingdom united Egypt under a single ruling house, developed systems of record-keeping, and formed an all-important caste of scribes, the royal bureaucrats who mastered hieroglyphic writing. Likewise, the essential characteristics of Egyptian religion emerged during the Old Kingdom, especially the idea that the king was actually a god and that his rule ensured that the world itself would continue – the Egyptians thought that if there was no king or the proper prayers were not recited by the priests, terrible chaos and destruction would reign on earth.
The Old Kingdom was stable and powerful, although its kings did not use that power to expand their borders beyond Egypt itself. Instead, all of Old Kingdom society revolved around the production of agricultural surpluses from the Nile, efficiently cataloged and taxed by the royal bureaucracy and “spent” on building enormous temples and, in time, tombs. The pyramids of Egypt were all built during the Old Kingdom, and their purpose was to house the bodies of the kings so that their spirits could travel to the land of the dead and join their fellow gods in the afterlife (thereby maintaining ma’at – sacred order and balance).
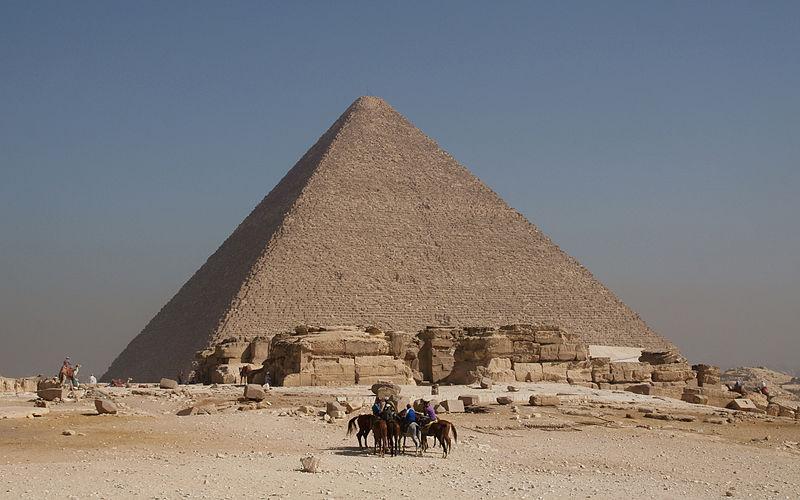

The pyramids are justly famous as the ultimate example of Egyptian prosperity and ingenuity. The Great Pyramid of Khufu, the single largest pyramid of the period, contained over 2.5 million stone blocks, each weighing approximately 2.5 tons. The sheer amount of energy expended on the construction of the pyramids is thus staggering; it was only the incredible bounty of the Nile and its harvests that enabled the construction of the pyramids by providing the calories consumed by the workers and draught animals, the wealth used to employ the supporting bureaucracy, and the size of the population that sustained the entire enterprise. Likewise, while the details are now lost, the Old Kingdom’s government must have been highly effective at tax collection and the distribution of food, supplies, and work teams. Pyramids on the scale of the Old Kingdom would have been all but impossible anywhere else in the world at the time.
A major factor in the stability of Old Kingdom Egypt was that it was very isolated. Despite its geographical proximity to Mesopotamia and Anatolia, Egypt at the time was largely separated from the civilizations of those regions. The Sinai Peninsula, which divides Egypt from present-day Palestine and Israel, is about 120 miles of desert. With a few violent exceptions, no major incursions were able to cross over Sinai, and contact with the cultures of Mesopotamia and the Near East was limited as a result. Likewise, even though Egypt is on the Mediterranean, sailing technology was so primitive that there was little contact with other cultures via the sea.
Around 2200 BCE, two hundred years after the last pyramids were built, the Old Kingdom collapsed, leading to the First Intermediate Period. The reason for the collapse is not clear, but it probably had to do with the very infrequent occurrence of drought. There are written records from this period of instability, known as the First Intermediate Period, that make it clear that Egyptians knew very well that things had been fundamentally upset and imbalanced, and they did not know what to do about it. The kings were supposed to oversee the harmony of life and yet the royal dynasty had collapsed without a replacement. This disrupted the entire Egyptian worldview.
In turn, this disruption prompted a development in Egyptian religion. The Egyptian religion of the Old Kingdom had emphasized life on earth; even though the pyramids were tombs built to house the kings and the things they would need on their journey to the afterlife, there are no records with details about how most people would fare after they died. This changed during the First Intermediate Period when the Egyptians invented the idea that the suffering of the present life might be overcome in a more perfect world to come. After death, the soul would be brought before a judge of the gods, who would weigh the heart on scales against the ideals of harmony and order. At this point, the heart might betray the soul, telling the god all of the sins its owner had committed in life. The lucky and virtuous person, though, would see their heart balance against the ideal of order and the soul would be rewarded with eternal life. Otherwise, their heart would be tossed to a crocodile-headed demon and devoured, the soul perishing in the process.
Monumental building ceased during the Intermediate Period – there were no more pyramids, palaces, or temples being built. A major social change that occurred was that royal officials away from the capital started to inherit titles, and thus it was the first time there was a real noble class with its own inherited power and land. Some historians have argued that a major cause of the collapse of royal authority was the growth in power of the nobility: in other words, royal authority did not fall apart first and lead to elites seizing more power, elites seized power and thereby weakened royal authority. The irony of the period is that the economy of Egypt actually diversified and expanded. It seems to have been a time in which a new elite commissioned royal-inspired goods and hence supported emerging craftspeople.
The Middle Kingdom was the next great Egyptian kingdom of the ancient world. The governor of the city of Thebes reunified the kingdom and established himself as the new king (Mentuhotep II, r. 2060 – 2010 BCE). One major change in Egyptian belief is that the Middle Kingdom rulers still claimed to be at least partly divine, but they also emphasized their humanity. They wrote about themselves as shepherds trying to maintain the balance of harmony in Egypt and to protect their people, rather than just as lords over an immortal kingdom. Their nobles had more power than had the nobility of the Old Kingdom as well, playing important political roles on their lands.
Starting during the Middle Kingdom, the kings made a major effort to extend Egyptian power and influence beyond the traditional “core” of the kingdom in Egypt itself. Egypt exerted military power and extracted wealth from the northern part of the kingdom of Nubia (in present-day Sudan) to the south, and also established at least limited ongoing contact with Mesopotamia as well. The kings actively encouraged immigration from outside of Egypt, but insisted that immigrants settle among Egyptians. They had the same policy with war captives, often settling them as farmers in the midst of Egyptians. This ensured speedy acculturation and helped bring foreign talent into Egypt.
While no more pyramids were ever built – it appears that the nearly obsessive focus on the spirit of the king after death was confined to the Old Kingdom – the Middle Kingdom was definitely a period of stability and prosperity for Egypt as a whole. A fairly diverse body of literature survived in the form of writings on papyrus, the form of paper made from Nile reeds monopolized by Egypt for centuries, that suggests that commerce was extensive, Egyptian religion celebrated the spiritual importance of ordinary people, and fairness and justice were regarded as major ethical imperatives.
Things spun out of control for the Middle Kingdom starting in about 1720 BCE, roughly 300 years after it had been founded, leading in turn to the Second Intermediate Period. Settlers from Canaan (present-day Jordan, Israel, Lebanon, and parts of Syria) had been streaming into Egypt for generations, initially settling and assimilating into Egyptian society. By about 1650 BCE, however, a group of Canaanites founded what was known as the “Hyksos” dynasty, an Egyptian term which simply means “leaders of foreigners,” after they overthrew the king and seized power in Lower Egypt. While they started as “foreigners,” the Hyksos quickly adopted the practices of the Egyptian kings they had overthrown, using Egyptian scribes to keep records in hieroglyphics, worshiping the local gods, and generally behaving like Egyptians.
The most significant innovation introduced by the Hyksos was the use of bronze (it should be noted that they introduced horses and chariots as well). There was very limited use of bronze in Egypt until the Second Intermediate Period, with both weapons and tools being crafted from copper or stone. Bronze, an alloy of copper and zinc or nickel, required technical skill and access to its component minerals to craft. The finished product was far harder and more durable than was copper alone, however, and with the advent of large-scale bronze use in Egypt thanks to the Hyksos, the possibilities for the growth of Egyptian power increased greatly. Bronze had already been in use for over a thousand years by the time it became common in Egypt, but when it finally arrived with Canaanite craftsmen it radically altered the balance of power. Up to that point, Egyptian technology, especially in terms of metallurgy, was quite primitive. Egyptian soldiers were often nothing more than peasants armed with copper knives, spears with copper heads, or even just clubs. Egypt’s relative isolation meant that it had never needed to develop more advanced weapons, a fact that the Hyksos were able to take advantage of, belatedly bringing the large-scale use of bronze with them.
In 1550 BCE, the Second Intermediate Period ended when another Egyptian king, Ahmose I, expelled the Hyksos from Egypt. Thus began the New Kingdom, the most powerful to date. This was also when the Egyptian kings started calling themselves pharaohs, which means “great house,” lord over all things. Using the new bronze military technology, the New Kingdom was (at times) able to expand Egyptian control all the way into Mesopotamia. Bronze was the key factor, but also important was the adoption of composite bows: bows that are made from strips of animal bone and sinew, glued together. A composite bow was much more powerful than a wooden one, and they greatly enhanced the power of the Egyptian military. Likewise, again thanks to the Hyksos, the New Kingdom was able to employ chariots in war for the first time. One in ten men was impressed into military service, supplemented with auxiliaries from conquered lands as well as mercenary forces.
While the Egyptians had always considered themselves to be the favored people of the gods, dwelling in the home of spiritual harmony in the universe, it was really during the New Kingdom that they actively campaigned to take over foreign lands. The idea was that divine harmony existed only in Egypt and had to be brought to the rest of the world, by force if necessary. By 1500 BCE, only 50 years after the founding of the new kingdom, Egypt had conquered Canaan and much of Syria. It then conquered northern Nubia. The pharaohs dispatched communities of Egyptians to settle conquered lands, both to pacify those lands and to exploit natural resources in order to increase royal revenue.
The New Kingdom pharaohs enlisted the leaders of the lands they had conquered as puppet kings, surrounded by Egyptian advisors. The pharaohs adopted the practice of bringing many foreign princes of the lands they had conquered back to Egypt. There, a prince would be raised as an Egyptian and educated to think of Egyptian civilization as both superior to others and their own. Thus, when they returned to rule after their fathers died, these princes would often be thoroughly assimilated to Egyptian culture and would naturally be more loyal to the pharaoh; using this technique, the New Kingdom was able to create several “puppet states,” places with their own rulers who were loyal to Egypt, in the Near and Middle East.
The New Kingdom was also the great bureaucratic empire of Egypt. The pharaohs divided Egypt into two administrative regions: Upper Egypt, up the Nile and governed from the city of Thebes, and Lower Egypt, near the Nile delta where it drained into the Mediterranean and ruled from the city of Memphis. Regional administrators did the important work of drafting laborers, extracting taxation, and making sure that agriculture was on track. A single royal official of vast personal power, the vizier, supervised the whole system and personally decided when to open the locks on the Nile to allow the floodwaters out each year.
While royal officials and the priesthoods of the gods held significant power and influence during the New Kingdom, the king (now known as the pharaoh) still ruled as a living god. The pharaohs were still thought to be divine, but that did not mean they simply bullied their subjects. Many letters have survived between pharaohs and their subordinates, as well as between pharaohs and other kings in foreign lands. They played tax breaks, gifts, and benefits off to encourage loyalty to Egypt rather than simply threatening people with divine power or armies.
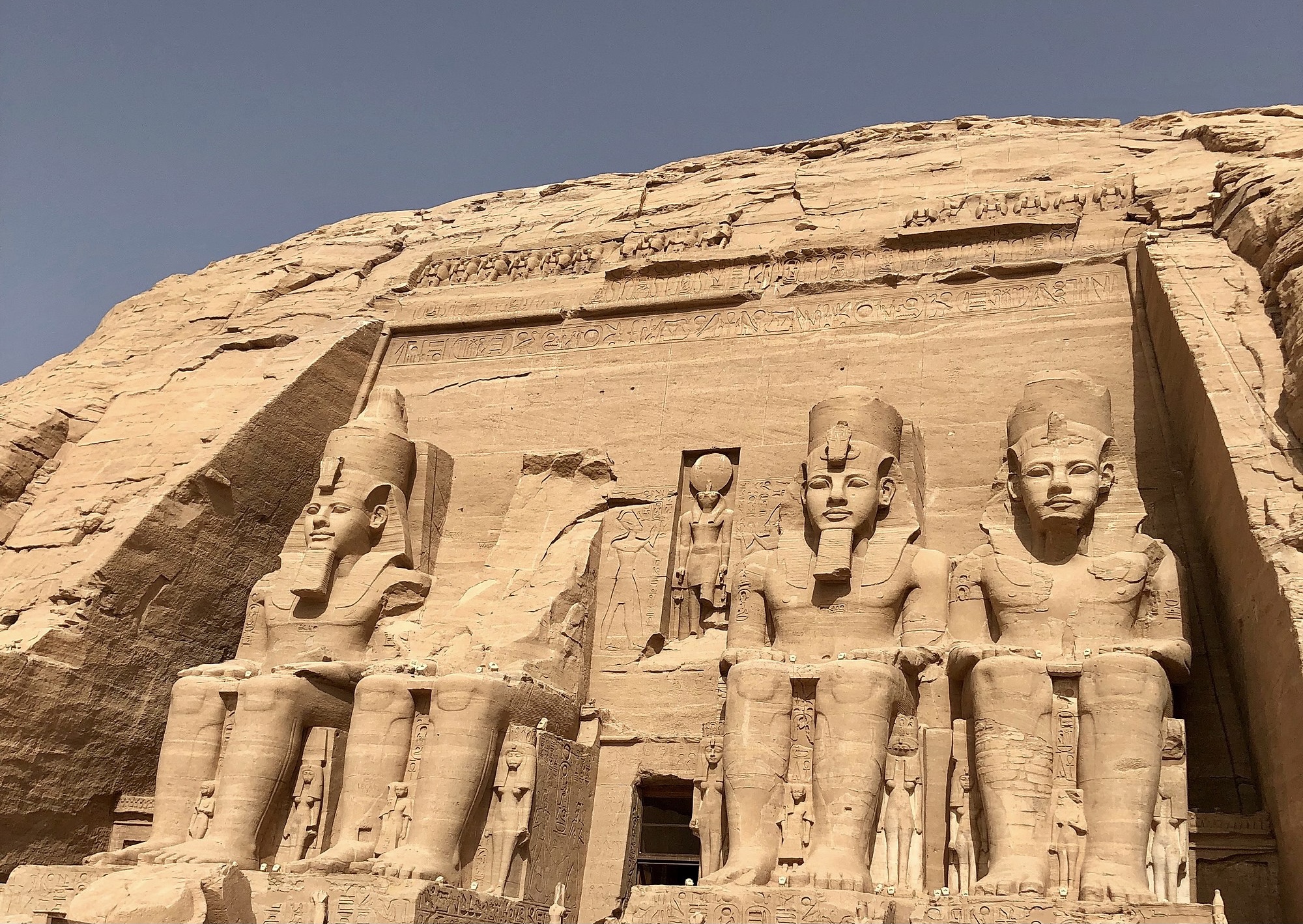
In addition to the New Kingdom’s expansionism, the governments pursued new forms of monumental architecture. While the construction of pyramids never occurred after the Old Kingdom, Egyptian kings remained focused on the creation of great buildings. They continued to build opulent tombs, but those were usually built into hillsides or in more conventional structures, rather than pyramids. The monumental architecture of the New Kingdom consisted of huge temples and statues, most notably the Great Temple at Abu Simbel in northern Nubia, built under the direction of the pharaoh Ramses II at some point around 1250 BCE. There, gigantic statues of the gods sit, and twice a year, the rising sun shines through the entrance and directly illuminates three of them, while the god of the underworld remains in shadow.

Detailed records of noteworthy pharaohs survive from the New Kingdom. The New Kingdom saw the only known female pharaoh, a woman who ruled from 1479 to 1458 BCE. Her name was Hatshepsut; she originally ruled as a regent (i.e. someone who is supposed to rule until the young king comes of age) for her stepson, but then claimed the title of pharaoh and ruled outright. She ruled for 20 years, waged war, and oversaw a period of ongoing prosperity. There were enormous building projects under her supervision, and it was also under her reign that large quantities of sub-Saharan African goods started to be imported from Nubia: gold, incense, live elephants, panther skins, and other forms of wealth. When she died, however, her stepson Thutmose III took the throne. Decades after he became pharaoh, for reasons that are unclear, he tried to erase the memory of his mother’s reign, perhaps driven by simple resentment over how long she had held power.
Another pharaoh of note was Amenhotep IV (r. 1353 – 1336 BCE). Amenhotep was infamous in his own lifetime for attempting an ill-considered full-scale religious revolution. He tried to focus all worship of the Egyptian people on an aspect of the sun god, Ra, called Aten. He went so far as to claim that Aten was the only god, something that seemed absurd to the resolutely polytheistic Egyptians. He renamed himself Akhenaten, which means “the one useful to Aten,” moved the capital to a new city he had built, sacked the temples of other gods, and even had agents chisel off references to the other gods from buildings and walls. All the while, he insisted that he and his queen, Nefertiti, be worshiped as gods themselves as the direct representatives of Aten. Historians do not know why he tried to bring about this religious revolution, but one reasonable theory is that he was trying to reduce the power of the priests, who had steadily become richer and more powerful over the centuries at the expense of the pharaohs themselves.
Akhenaten’s attempted revolution was a disaster. In the eyes of common people and of later pharaohs, he had fundamentally undermined the very stability of Egypt. In the eyes of his subjects, the royal person was no longer seen as a reliable spiritual anchor – the pharaoh was supposed to be the great protector of the religious and social order, but instead one had tried to completely destroy it. This was the beginning of the end of the central position the pharaoh had enjoyed in the life of all Egyptians up until that point.
Akhenaten’s son restored all of the old religious traditions. This was the young king Tutankhamun (“King Tut”) (r. 1336 – 1326), who is important for restoring the religion and, arguably, for the simple fact that his tomb was never looted by grave robbers before it was discovered by a British archaeologist in 1922 CE. It provided the single most significant trove of artifacts from the New Kingdom yet found when it was discovered, sparking an interest in ancient Egyptian history all over the world.

A new dynasty of pharaohs ruled the New Kingdom in the aftermath of Akhenaten’s disastrous experiment, the most powerful of which was Ramses II (r. 1279 – 1213). Ramses campaigned against the growing power of an empire in the north called the Hittites, one of the major empires of the Bronze Age period (considered in more detail in the next chapter). He ruled for an astonishingly long time and reputedly sired some 160 children with wives and concubines. He also supervised the construction of the Great Temple of Abu Simbel noted above. Ramses was, however, the last of the great pharaohs, with all of those who followed working to stave off disaster more so than expand Egyptian power.
The New Kingdom collapsed in about 1150 BCE. This collapse was part of a much larger pattern across the ancient Middle East and North Africa: the collapse of the Bronze Age itself. In the case of Egypt, this took the form of the first of a series of foreign invasions, that of the “Sea People,” whose origins have never been determined despite concentrated scholarship on the question. Later, invaders referred to as “gangs of bandits” from what is today Libya, to the west of Egypt, further undermined the kingdom, and it finally fell into a long period of political fragmentation. A long period of civil war and conflict engulfed Egypt, and from that point on Egypt proved vulnerable to foreign conquest. In the course of the centuries that followed Assyria, Persia, the Greeks, and the Romans would, one after the other, add Egypt to their respective empires.
Questions for Discussion
What kinds of forces seemed to interrupt the stability of the Ancient Egyptian dynasties during the intermediate periods?
How do the Egyptian political leaders such as Hatshepsut, Amenhotep IV (a.k.a. Akhenaten), Tutankhamun, or Ramses II either surprise or challenge the notion that Egypt was “remarkably stable and consistent” for thousands of years as described at the start of the chapter?
2.3 Continuities in Egyptian History
The long-term pattern in Egyptian history is that there were long periods of stability and prosperity disrupted by periodic invasions and disasters. Throughout the entire period, however, there were many cultural, spiritual, and intellectual traditions that stayed the same. In terms of the spiritual beliefs of the ancient Egyptians, those traditions most often focused on the identity and the role of the king in relation to the gods. In prosaic politics and social organization, they revolved around the role of the scribes. In terms of foreign relations, they evolved over time as Egypt developed stronger ongoing contacts with neighboring states and cultures.
Key Terms 2.3-2.4
- scribes
- monumental architecture
- redistributive economy
- serfs
- Nubia
The most important figure in Egyptian spiritual life was the king; he (or sometimes she) was believed to form a direct connection between the gods and the Egyptian people. Each king had five names – his birth name, three having to do with his divine status, and one having to do with rulership of the two unified kingdoms. One of the divine names referred to the divine kingship itself, temporarily linked to the current holder of that title: whoever happened to be king at the time.
The Egyptians had a colorful and memorable set of religious beliefs, one that dominated the lives of the kings, who claimed to be not just reflections of or servants of the gods, but gods themselves on earth. The central theme among the great epic stories of Egyptian religion was that there was a certain order and harmony in the universe that the gods had created, but that it was threatened by forces of destruction and chaos. It was the job of humans, especially Egyptians, to maintain harmony through proper rituals and through making sure that Egyptian society was stable. For Egyptians the world was divided between themselves and everyone else. This was not just a function of arrogance, however, but instead reflected a belief that the gods had designated the Egyptians to be the sacred keepers of order.
One peculiar aspect of the obsessive focus on the person of the king was the fact that the kings often married their sisters and daughters; the idea was that if one was a god, one did not want to pollute the sacred bloodline by having children with mere humans. An unfortunate side effect was, not surprisingly, that there were a lot of fairly deranged and unhealthy Egyptian royalty over the years, since the royal lines were, by definition, inbred. Fortunately for the Egyptian state, however, the backbone of day-to-day politics was the enormous bureaucracy staffed by the scribal class, a class that survived the entire period covered in this chapter.
More writing survives from ancient Egypt than any other ancient civilization of the Mediterranean region. There are two major reasons for that survival. First, Egypt’s dry climate ensured that records kept on papyrus had a decent chance of surviving since they were unlikely to rot away. Thousands of papyri documents have been discovered that were simply dumped into holes in the desert and left there; the sand and the climate conspired to preserve them. Second, Egypt developed an important social class of scribes whose whole vocation was mastering the complex Egyptian writing systems and keeping extensive records of almost every aspect of life, from religious ritual to mundane record-keeping.

The writing of ancient Egypt was in hieroglyphics, which are symbols that were adapted over time from pictures. There were several different forms of hieroglyphics, including two distinct alphabets during the period covered in this chapter, all of which were very difficult to master. It took years of training to become literate in hieroglyphics, training that was only afforded to the scribes. Scribes recorded everything from tax records, to mercantile transactions, to the sacred prayers for the dead on the walls of the tombs of kings and nobles. They served as an essential piece of the continuity of Egyptian politics and culture for thousands of years. In other words, because they used the same language and the same alphabets of symbols, and because they recorded the rituals and transactions of Egyptian society, scribes were a kind of cultural glue that kept things going from generation to generation. In all three of the great dynasties and during the Intermediate Periods, it was the scribes who provided continuity.
As iconic as hieroglyphic writing, which remains famous because of the sheer amount of it that survived carved in stone in tombs and palaces, was the creation of monumental architecture by the Egyptian state, first exemplified by the pyramids. Sometime around 2660 BCE the first pyramid was built for the king Djoser. Djoser was renowned in the Egyptian sources for his wisdom, and centuries after his death he became a legendary figure to later Egyptians. The architect who designed the pyramid, Imhotep, was later deified as a son of Ptah, the god who created the universe. Unlike Mesopotamian ziggurats, which were always temples, the pyramids were always tombs. The purpose of the pyramids was to house the king with all of the luxuries and equipment he would need in his journey to the afterlife, as well as to celebrate the king’s legacy and memory.
The pyramids were constructed over a period of about 250 years, from 2660 to 2400 BCE. For a long time, historians thought that they were built by slaves, but it now seems very likely that they were built by free laborers employed by the king and paid by royal agents. Each building block weighed about 2.5 tons and had to be hauled up ramps with ropes and pulleys. As noted above, only Egypt’s unique access to the bounty of the Nile provided enough energy for this to be viable. Egypt was the envy of the ancient world because of its incredible wealth, wealth that was the direct result of its huge surplus of grain, all fed by the Nile’s floods. The pyramids were built year-round, but work was most intense in September, when the floods of the Nile were at their height and farmers were not able to work the fields. In short, nowhere else on earth could the pyramids have been built. There had to be a gigantic surplus of energy in the form of calories available to get it done.
Pyramid building itself was the impetus behind the massive expansion of bureaucracy in the Old Kingdom, since the state became synonymous with the diversion and redistribution of resources needed to keep an enormous labor force mobilized. The king could, in theory, requisition anything, mobilize anyone, and generally exercise total control, although practical limits were respected by the administration. Since there was no currency, “payment” to scribes usually took the form of fiefs (i.e. grants of land) that returned to the royal holdings after the official’s death, a practice that atrophied after the fall of the Old Kingdom.
Like their neighbors in Mesopotamia, the Egyptians lived in a redistributive economy, an economy in which crops were taken directly from farmers (i.e. peasants) by the agents of the king and then redistributed. Appropriately enough, many of the surviving documents from ancient Egypt are tax records, carefully recorded in hieroglyphics by scribes. Peasants in Egypt were tied to the land they lived on and were thus serfs rather than free peasants. A serf is a farmer who is legally tied to the land he or she works on – they cannot leave the land to look for a better job elsewhere, living in a state very near to slavery. The peasants lived in “closed” villages in which people were not allowed to move in, nor were existing families supposed to move out.
Interestingly, unlike many other ancient societies, women in Egypt were nearly the legal equals of men. They had the legal right to own property, sue, and essentially exist as independent legal entities. This is all the more striking in that many of the legal rights that Egyptian women possessed were not available to women in Europe (or the United States) until the late 1800s CE, over three thousand years later. Likewise, Egyptian women enjoyed much more legal autonomy than did women in many other ancient societies, particularly that of the Greeks.
Even though the essential characteristic of Egyptian religion and social structure was continuity, its relationships with neighboring cultures did change over time. One important neighbor of Egypt was the kingdom of Nubia to the south, in present-day Sudan. Nubia was rich in gold, ivory, and slaves, seized from neighboring lands, making it a wealthy and powerful place in its own right. Egypt traded with Nubia, but also suffered from raids by warlike Nubian kingdoms. One of the key political posts in Egypt was the Keeper of the Gateway of the South, a military governor who tried to protect trade from these attacks. At the start of the Middle Kingdom, Mentuhotep II managed to not only reunite Egypt, but to conquer the northern portion of Nubia as well. Kings continued this pattern, holding on to Nubian territory and building a series of forts and garrisons to ensure the speedy extraction of Nubian wealth. (Much later, a Nubian king, Piankhy, returned the favor by conquering Egypt – he claimed to be restoring a purer form of Egyptian rule than had survived in Egypt itself!)
Trade contact was not limited to Nubia, of course. Despite the fact that the Egyptians thought of themselves as being superior to other cultures and civilizations, they actively traded with not only Nubia but the various civilizations and peoples of the Near and Middle East. Starting in earnest with the Middle Kingdom, trade caravans linked Anatolia, Mesopotamia, and Egypt (and, later, Greece as well). There was a rich diplomatic exchange between the Egyptian kings and the kings of their neighboring lands – overall, they spent far more time trading with their neighbors and sending one another gifts than waging war. Likewise, as noted above in the section on the New Kingdom, military expansionism did not preclude Egypt’s membership in a “brotherhood” of other states during the Bronze Age.
That being said, by the time of the Middle Kingdom, there was an organized and fortified military presence on all of Egypt’s borders, with particular attention to Nubia and “Asia” (i.e. everything east of the Sinai Peninsula). One king described himself as the “throat-slitter of Asia,” and all the way through the New Kingdom, Egyptians tended to regard themselves as being the most important and “central” civilization in the world.
2.4 Conclusion
This chapter concludes its detailed consideration of Egypt with the fall of the New Kingdom not because Egyptian civilization vanished, but because it did not enjoy lasting stability under a native Egyptian dynasty again for most of the rest of ancient history. Instead, after the New Kingdom, Egypt was often torn between rival claimants to the title of pharaoh, and beginning with a civilization discussed in the next chapter, the Assyrians, Egypt itself was often conquered by powerful rivals. It is important to bear in mind, however, that Egypt remained the richest place in the ancient world because of the incredible abundance of the Nile, and whether it was the Assyrians, the Persians, the Greeks, the Romans, or the Arabs doing the conquering, Egypt was always one of the greatest prizes that could be won in conquest. Likewise, Egypt contributed not just wealth but its unique culture to the surrounding regions, serving as one of the founding elements of Western Civilization as a whole.
Questions for Discussion
Compare and contrast the Mesopotamian and Egyptian societies. What are the causes of any differences or similarities you find?
What elements of Egypt’s geography helped to create a predictable and stable environment and how did that impact Egypt’s culture and society?
What is the evidence for the major differences in the position and treatment of women in Egyptian society compared to other ancient world societies? What might account for this historical difference?
Do you think this civilization would have been as stable or as long-lasting without the abundance of resources, particularly food, that their extraordinary geographical setting provided?
Further Resources
Dr. Amy Calvert, “The Great Pyramids of Giza,” in Smarthistory, August 8, 2015, accessed July 10, 2021, https://smarthistory.org/the-great-pyramids-of-giza/.
Dr. Beth Harris and Dr. Steven Zucker, “Mortuary Temple and Large Kneeling Statue of Hatshepsut,” in Smarthistory, August 9, 2015, accessed July 10, 2021, https://smarthistory.org/hatshepsut/.
Joshua J. Mark, “Akhenaten” in World History Encyclopedia, April 17, 2014, accessed July 10, 2021, https://www.worldhistory.org/Akhenaten/.
Joshua J. Mark, “Women in Ancient Egypt” in World History Encyclopedia, November 4, 2016, accessed July 10, 2021, https://www.worldhistory.org/article/623/women-in-ancient-egypt/.
Image Citations (Wikimedia Commons):
Egypt map – Jeff Dahl
Great Pyramid – Kallerna
Great Temple of Ramses II at Abu Simbel – Warren LeMay
Tutankhamun’s coffin – D. Denisenkov
Hieroglyphics – Sherif217
