2.6 Biological Theories and Therapies
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define biological theories and therapies
- Identify nursing application of biological theories and therapies
From a biological perspective, mental health conditions are considered physiological disorders with a focus on the neurological and immune systems of the body, as well as genetic components of health. Trauma and injury are also considered with diagnoses and treatment of mental illness (Schwartz & Corcoran, 2017). Magnetic and computerized imaging are used to study the brain and detect areas of damage or change. The premise is to find where the problem is in the brain and target that area with medications, diet, surgery, or other therapies, such as brain stimulation.
Definitions of Biological Treatments
Biological theory centers on an actual physical reason for psychiatric problems and, in effect, has decreased the stigma long associated with mental illness. For instance, when a person is diagnosed with schizophrenia, under this theory it has a physical root cause, which displaces any blame.
Medication Therapy
Biological therapy provides remedies for mental health disorders by physically treating the brain. Medical understanding of the action of neurotransmitters in the brain provides the rationale for pharmacological approaches. Intended to restore balance in this chemical process, medication therapy is the most commonly utilized method to treat mental health disorders.
Using chemicals to adjust the brain chemistry to assist the client with a mental health disorder is psychopharmacology. With the inception of chlorpromazine, also known as Thorazine, a strong antipsychotic medication, in 1952, many psychiatric clients were able to move from a state of psychosis to a manageable lifestyle (Lindamood, 2005). Medications that target neurotransmitters help restore brain function by regulating these neurotransmitters. Clients report having less emotional distress and greater satisfaction with their lives, due to taking these medications. Clinicians began to understand the vital role these chemicals provided as a new way to treat psychiatric disorders, other than simply psychoanalysis and behavioral therapy. Many medications have proven effective to treat and/or control psychosis, mania, depression, and anxiety. These medications have decreased lengths of hospitalization and helped clients lead more productive lives.
Diet
Healthy lifestyles include healthy diets. Research has found evidence of dietary influence on mental health. Grajek et al. (2022) reviewed possible connections between nutrition and mental health. Nutrition may be able to reduce inflammatory processes in the body and promote optimal circulatory and cellular health. Studies reviewed by Grajek et al. (2022) found that complex carbohydrates, antioxidants, vitamins B9, D, E, C, carotenoids, tryptophan, alpha-lipoic acid, and soluble fiber could have these therapeutic effects. Recent research describes new disciplines of psychodietetics and nutritional psychiatry (Grajek et al., 2022).
Psychosurgery
Neurosurgery intended to alter psychological responses is called psychosurgery (De Jesus et al., 2023). It can be used for a select group of clients who have not experienced successful treatment for anxiety disorders, major depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorders. Psychosurgery alters small portions of brain tissue in specific areas that control certain behaviors. Changes are made by thermal, radiation, or surgical methods without damage to the person’s general function. Drastic surgeries such as frontal lobotomy are no longer performed due to disabling effects.
Brain Stimulation/ECT
Brain stimulation therapies are those that stimulate the brain through neurochemicals, electricity, and nerve action (National Alliance on Mental Illness [NAMI], 2023). There is traditional electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), which uses electricity to stimulate targeted areas of the brain by creating a controlled seizure, most commonly used to treat major depression. Now other brain stimulation therapies, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), aim to target specific brain areas to treat the problem. These therapies also treat other disorders, such as epilepsy, Parkinson disease, and several chronic pain disorders.
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) uses an electric current to create a generalized cerebral seizure. Although it is primarily utilized to treat patients with severe depression, patients with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, catatonia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and bipolar disorder may also benefit. However, the practice has a stigma attached to it due to misinformation regarding procedural methodology.
Link to Learning
Learn more about ECT from StatPearls.
Complementary and Alternative Treatments (CAM)
More than 30 percent of adults and about 12 percent of children—use health care approaches that are not typically part of conventional medical care or that may have origins outside of usual Western practice. When describing these approaches, people often use “alternative” and “complementary” interchangeably. (National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, 2021) (Figure 2.4)
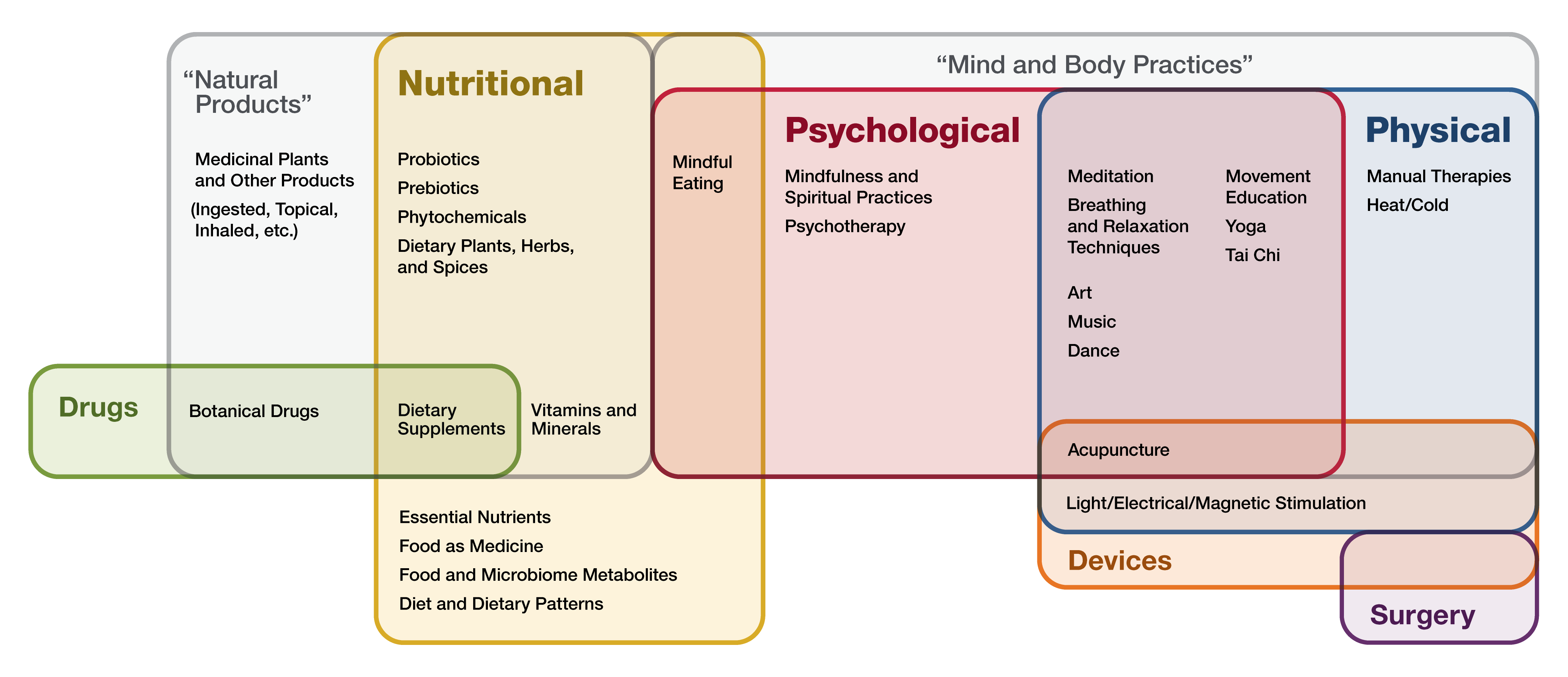
Nursing Application of Biological Theory
The major concepts of the biological theory related to nursing are basic care of the client, through monitoring and supporting their physical needs. Nurses are responsible for overseeing sleep, activity, nutrition, hydration, elimination, and other functions for the client. The nurse is responsible for administering medications and preparing the client for procedures. The nurse also monitors drug-level laboratory reports and ensures the client’s therapeutic level is met. This physical care of the psychiatric client is part of the holistic approach nursing is known for.
For clients in treatment with biological therapies, teaching is a nursing intervention that promotes health, prevents harm, and empowers the client through partnership with the health-care team. Specific to medication teaching, clients must be made aware of the indications and effects of all medications prescribed, including over-the-counter and drug-food interactions. Nurses also conduct preoperative or pre-procedure teaching and witness the surgical or procedural written consent. This education contributes to the effectiveness of the plan of care.
In dietary education, nurses can teach how stress can result in food choices detrimental to overall health and educate clients on the aspects of emotional eating, where food becomes a substitute for addressing feelings. Nurses can counsel on grocery shopping and meal preparation. Nurses also play a supportive role as advocates for the expressed preferences of the client in treatment with biological therapies. The client’s beliefs and values must be considered and explored. Open exchange of this information contributes to best outcomes of care. Clients and families must be informed of aspects of all biological therapies.
Link to Learning
The Use of Theories in Psychiatric Nursing-II discusses all the major theories reviewed in this chapter and how nurses can use them in practice.
Link to Learning
This article from Sutter Health discusses how proper nutrition can enhance mental health, and poor nutrition can negatively affect thinking and energy level.
Media Attributions
- nutritional-psychological-physical-venn-diagram-08-01-crop
centers on an actual physical reason for psychiatric problems
using chemicals to regulate brain chemistry to assist the client with mental health disorders
The study of diet and psychiatric illnesses.
neurosurgery intended to alter psychological responses
ECT uses an electric current to create a generalized cerebral seizure to control some mental illnesses which do not respond to other treatments.
